Topological Sorting in DAGs
Topological Sorting :
Topological sorting for Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is a linear odering of vertices such that for every directed edge (u,v) vertex u come before v in the odering. Topological sorting for a graph is not possible if the graph is not a DAG.
For instance, the vertices of the graph may represent tasks to be performed, and the edges may represent constraints that one task must be performed before another.
Applications of Topological Sorting :
- Scheduling jobs from the given dependencies among jobs.
- Operation System deadlock detection.
- Dependency resolution: Suppose, A class extends B class. Then B has a dependency on A, and A must be compiled before B.
- Critical path analysis is a project management technique. It is used to find the minimum time a project can take and the dependencies of each activity on others.
- Determining the order of compilation tasks to perform in make files, data serialization, and resolving symbol dependencies in linkers.
Visualize here.
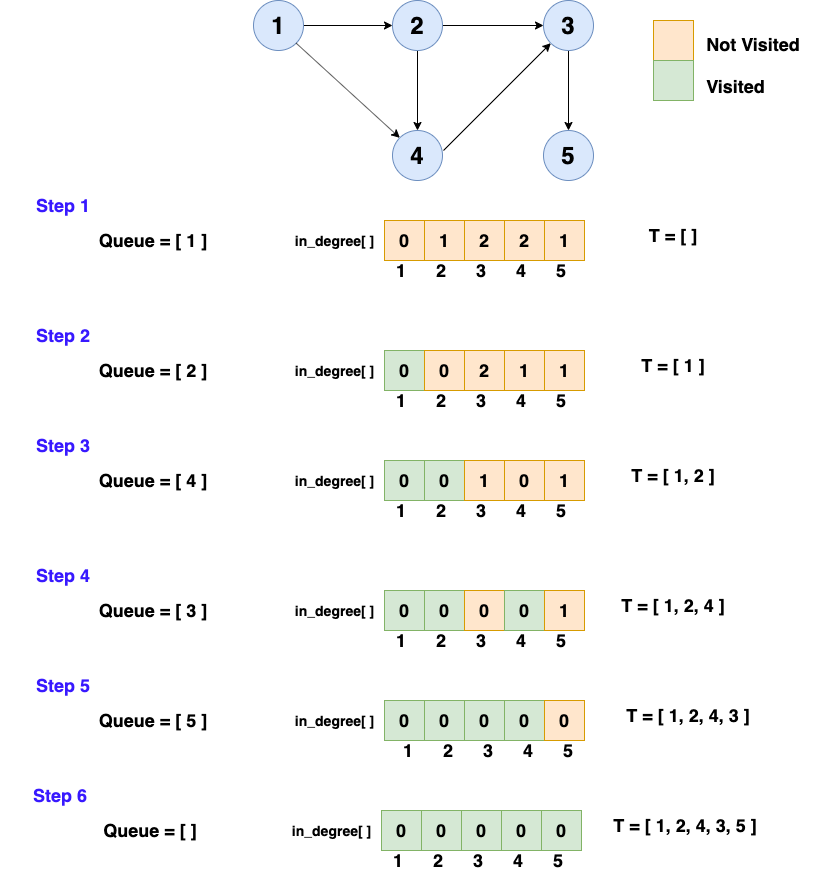
Topological sorting using BFS (Kahn’s Algorithm) :
in_degree - No. of edges towards the node.
Algorithm steps:
- Compute in-degree (number of incoming edges) for each of the vertex present in the DAG and initialize the count of visited nodes as 0.
- Pick all the vertices with in-degree as 0 and add them into a queue
- Remove a vertex from the queue (Dequeue operation) and then :
- Increment count of visited nodes by 1.
- Decrease in-degree by 1 for all its neighbouring nodes.
- If in-degree of a neighbouring nodes is reduced to zero, then add it to the queue.
- Repeat Step 3 until the queue is empty.
- If count of visited nodes is not equal to the number of nodes in the graph then the topological sort is not possible for the given graph.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Graph {
int V;
list<int> *l;
public:
Graph(int v) {
V = v;
l = new list<int>[V];
}
void addEdge(int i, int j, bool undir = false) {
l[i].push_back(j);
if (undir) l[j].push_back(i);
}
void topologicalSort() {
vector<int> indegree(V, 0);
// Iterate over all the edges to find the right indegree
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
for (auto nbr : l[i]) indegree[nbr]++;
}
// bfs
queue<int> q;
// init the q with nodes having 0 indegree
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if (indegree[i] == 0) q.push(i);
}
// start popping
while (!q.empty()) {
int node = q.front();
cout << node << " ";
q.pop();
// iterate over the nbrs of this node and reduce their indegree by 1
for (auto nbr : l[node]) {
indegree[nbr]--;
if (indegree[nbr] == 0) q.push(nbr);
}
}
}
};
int main() {
Graph g(5);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 3);
g.addEdge(1, 3);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(3, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 4);
g.topologicalSort(); //0 1 3 2 4
return 0;
}
Topological sorting using DFS :
Alogrithm steps :
- Create the graph by calling addEdge(a,b).
- Call the dfsTopologicalSort( )
- Create a stack and a boolean array named as visited[ ];
- Mark all the vertices as not visited i.e. initialize visitedwith 'false' value.
- Call the recursive helper function dfs() to store Topological Sort starting from all vertices one by one.
- Inside dfs function :
- Mark the current node as visited.
- Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex.
- Push current vertex to stack which stores result.
- Atlast after return from the helper function, print contents of stack.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Graph {
int V;
list<int> *l;
public:
Graph(int v) {
V = v;
l = new list<int>[V];
}
void addEdge(int i, int j, bool undir = false) {
l[i].push_back(j);
if (undir) l[j].push_back(i);
}
void dfs(int node, vector<bool> &visited, list<int> &ordering) {
visited[node] = true;
for (int nbr : l[node]) {
if (!visited[nbr]) dfs(nbr, visited, ordering);
}
// at this point we are backtracking
ordering.push_front(node);
return;
}
void dfsTopologicalSort() {
vector<bool> visited(V, false);
list<int> ordering;
// call dfs from node if not visited
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) dfs(i, visited, ordering);
}
for (auto a : ordering) {
cout << a << " ";
}
}
};
int main() {
Graph g(5);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 3);
g.addEdge(1, 3);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(3, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 4);
g.dfsTopologicalSort(); // 0 1 3 2 4
return 0;
}