MYSQL Queries Basics
Content of this post are notes taken from this freecodecamp video.



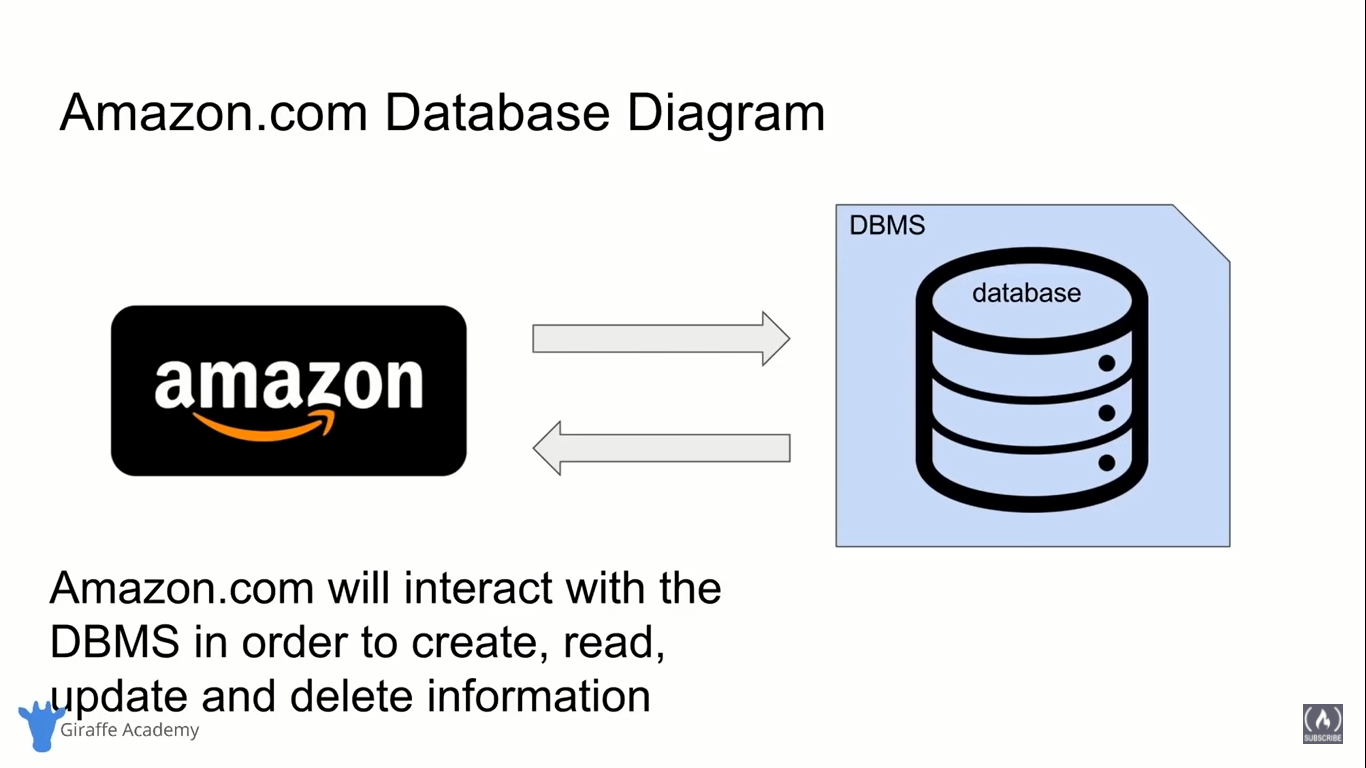

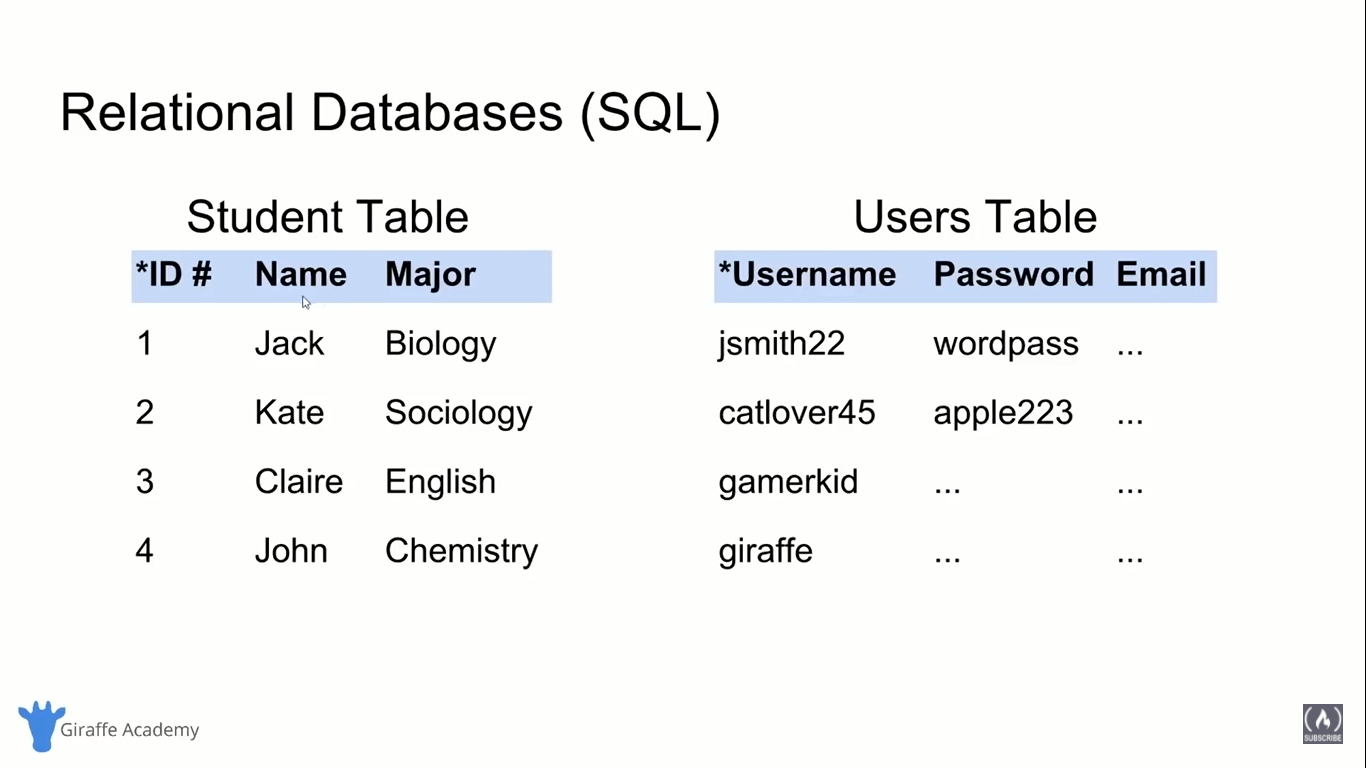
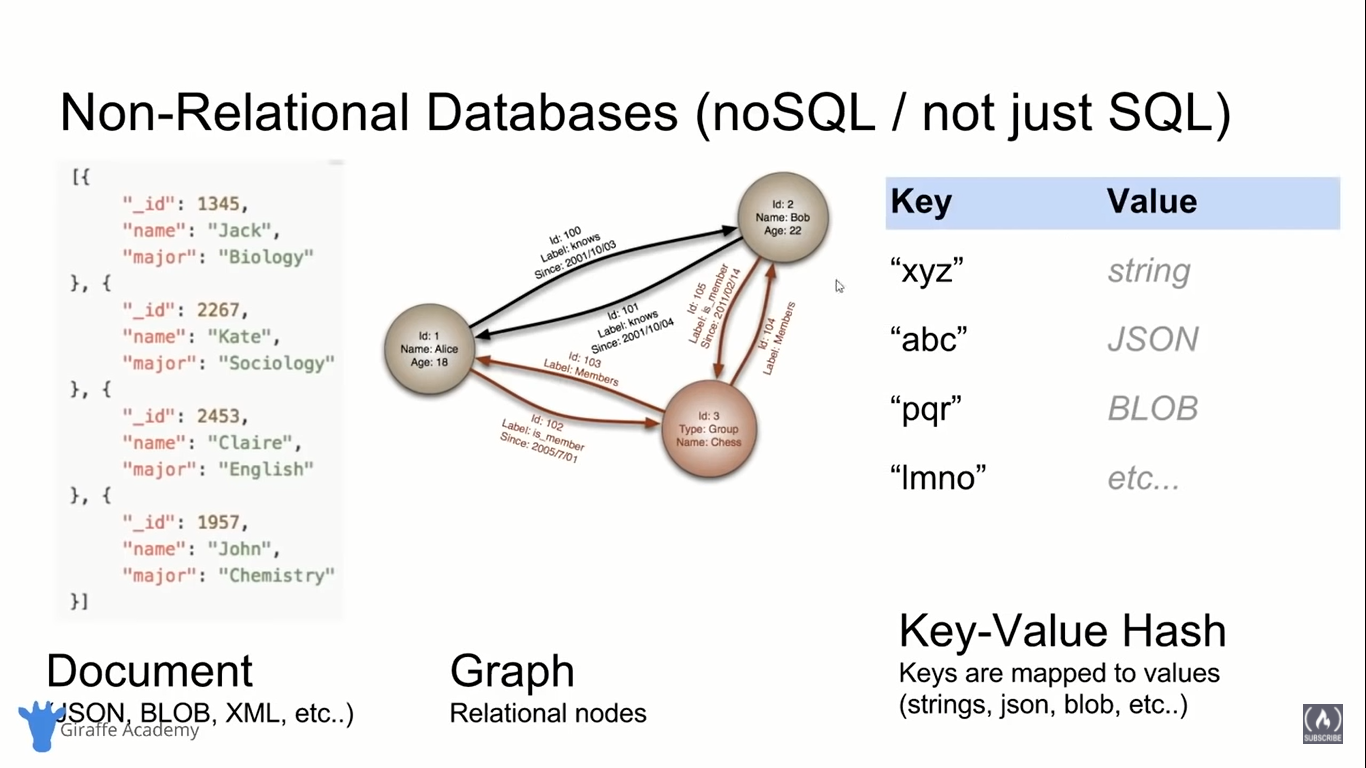



Tables and Keys in RDBMS
- It have rows and columns.
- We have a primary key which helps in uniquely identifying a specific row in database.
| Student id (p) | name | major | Branch id (f) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jayesh | Mathematics | 11 |
| 2 | Jay | Biology | 12 |
| 2 | Jayesh | Mathematics | 11 |
Here both Jayesh are different and can be identified by student id (primary key).
- Here, student id is a Surrogate Key and a surrogate key is basically a key that has no mapping to anything in the real world. Just random number.
- We can also use Natural Keys instead of surrogate keys. A natural key is a key that has significance in real world. For example :- SSN(social security number), our own roll number 19T5030 as it gives so much info about my academics.
- Another key is Foreign Keys. And a foreign key is an attribute that we can store on a database table that will link us to another database table. Here Branch can work as a foreign key.
| Branch | Strength | Class Teacher | Branch id |
|---|---|---|---|
| E&TC | 78 | John | 11 |
| CSE | 72 | Kate | 12 |
Here branch id is linking us to another table
- Foreign Keys can also be used to define relationship in same table. Example :- In a database of employees, some employees can be the manager of others.
- Primary key can also consists of more than one columns, and this is what we would call Composite keys. A composite key is a key that needs two attribute.
| Branch | Teacher | Subject |
|---|---|---|
| 11 | John | Java |
| 11 | Kate | C++ |
| 12 | Kate | C++ |
Here branch id and teacher both works as primary key i.e. they together are composite key.
-
Color values
Primary key
Foreign key
Composite key
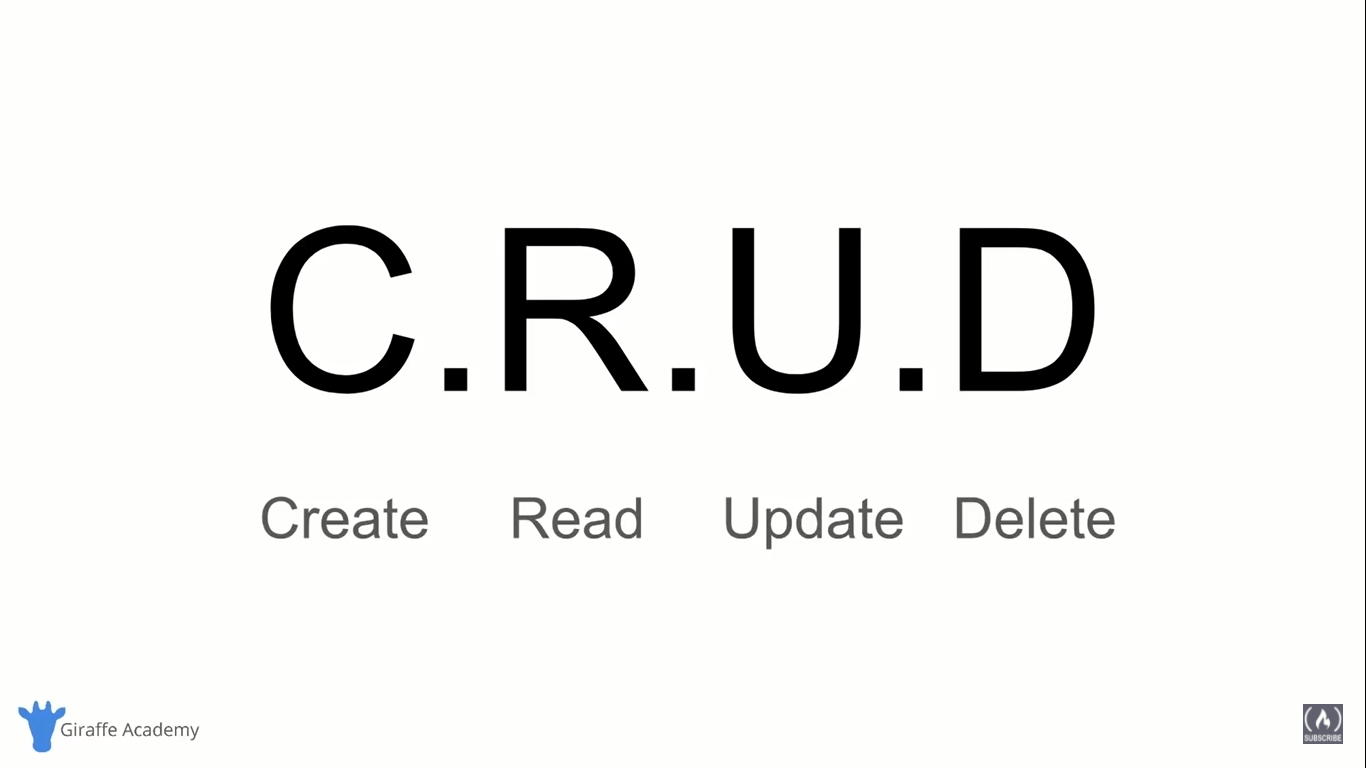
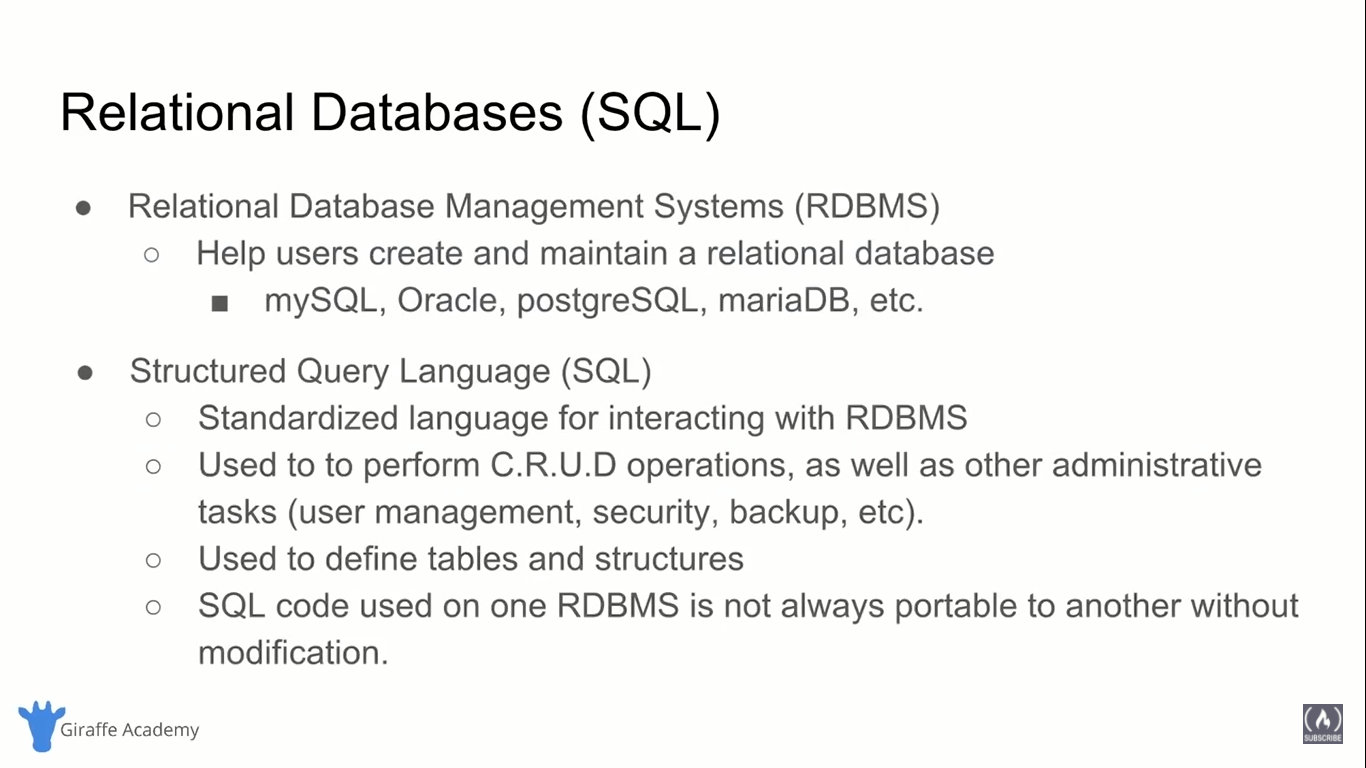
Structured Query Language (SQL) ➖



Queries
- A query is a set of instructions given to the RDBMS (written in SQL) that tell the RDBMS what information you want it to retrieve for you.
- Tons of data in database.
- Often hidden in a complex schema.
- Goal is to only get the data you need.
SELECT employee.name, employee.age
FROM employee
WHERE employee.salary > 3000;
Creating Tables
Datatypes :
INT -- Whole Numbers
DECIMAL(M,N) -- Decimal Numbers with M total digits, N digits after decimal
VARCHAR(l) -- String of text of length l
BLOB -- Binary Large Object, Stores large data
DATE -- 'YYYY-MM-DD'
TIMESTAMP -- 'YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS
Let's create a table -
CREATE TABLE student (
student_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(20),
major VARCHAR(20)
);
or
CREATE TABLE student (
student_id INT,
name VARCHAR(20),
major VARCHAR(20),
PRIMARY KEY(student_id)
);
This will create -
| student_id (p) | name | major |
|---|---|---|
DESCRIBE student;
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| student_id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| name | varchar(20) | YES | NULL | ||
| major | varchar(20) | YES | NULL |
- To Delete Table -
DROP TABLE student;
- Add a column to the Table -
ALTER TABLE student ADD gpa DECIMAL(4,2);
- Delete a column of the Table -
ALTER TABLE student DROP COLUMN gpa;
Inserting Data in Table -
INSERT INTO student VALUES(
1, 'Jack', 'Biology'
);
- See Table values -
SELECT * FROM student;
| student_id (p) | name | major |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jack | Biology |
INSERT INTO student(student_id, name) VALUES(2, 'Kate');
| student_id (p) | name | major |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jack | Biology |
| 2 | Kate | NULL |
Constrains -
- Make fields Required -
CREATE TABLE student (
student_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL, -- NOT NULL
major VARCHAR(20)
);
- Make fields Unique -
CREATE TABLE student (
student_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(20) UNIQUE, -- UNIQUE
major VARCHAR(20)
);
- PRIMARY KEY is NOT NULL and UNIQUE by default.
- We want to set a default value -
CREATE TABLE student (
student_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(20),
major VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT 'undecided' -- default string value undecided
);
- We are increasing PRIMARY KEY on each entry, we can also make db do that -
CREATE TABLE student (
student_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT, -- Now we don't need to enter id
name VARCHAR(20),
major VARCHAR(20),
PRIMARY KEY(student_id)
)
Update and Delete -
- What if we want to change some information from database -
UPDATE student
SET major = 'Bio'
WHERE major = 'Biology';
-- this will change all Biology major fields to Bio
- Other comparison operations -
| = | equal |
| <> | not equal |
| > | greater than |
| < | less than |
| >= | greater than or equal |
| <= | less than or equal |
UPDATE student
SET major = 'Biochemistry'
WHERE major = 'Bio' OR major = 'Chemistry';
-- obvious
UPDATE student
SET name = 'Tom', major = 'undecided'
WHERE student_id = 1;
-- obvious
- If we remove WHERE statement, then it will get applied to every column of table -
UPDATE student
SET major = 'Science';
- Delete row from table -
DELETE FROM student; -- This will delete all the rows from the table
DELETE FROM student
WHERE student_id = 5; -- Delete a specific row
DELETE FROM student
WHERE name = 'Tom' AND major = 'Bio';
Basic Queries -
Getting information from database.
- Grab all the information -
SELECT * FROM student;
- Grab a column -
SELECT name FROM student;
- Grab multiple columns -
SELECT name, major FROM student;
or
SELECT student.name, student.major FROM student;
- Sort by values -
SELECT name, major
FROM student
ORDER BY name;
SELECT name, major
FROM student
ORDER BY name DESC; -- For descending order && ASC for ascending
SELECT name, major
FROM student
ORDER BY student_id; -- even though we are not selecting id we can order by it
SELECT name, major
FROM student
ORDER BY major, student_id; -- first sort by major then student_id
- Limit number of result -
SELECT *
FROM student
LIMIT 2; -- gonna show only two result
- Filtering -
SELECT *
FROM student
WHERE major = 'Chemistry'; -- fiter
SELECT *
FROM student
WHERE major = 'Chemistry' OR major = 'Biology'; -- fiter
-- We can use a bunch of comparison operators in WHERE
-- <, >, <=, >=, <>
SELECT *
FROM student
WHERE name IN ('Claire', 'Kate', 'Mike'); -- domains
-- we can always combine all the queries
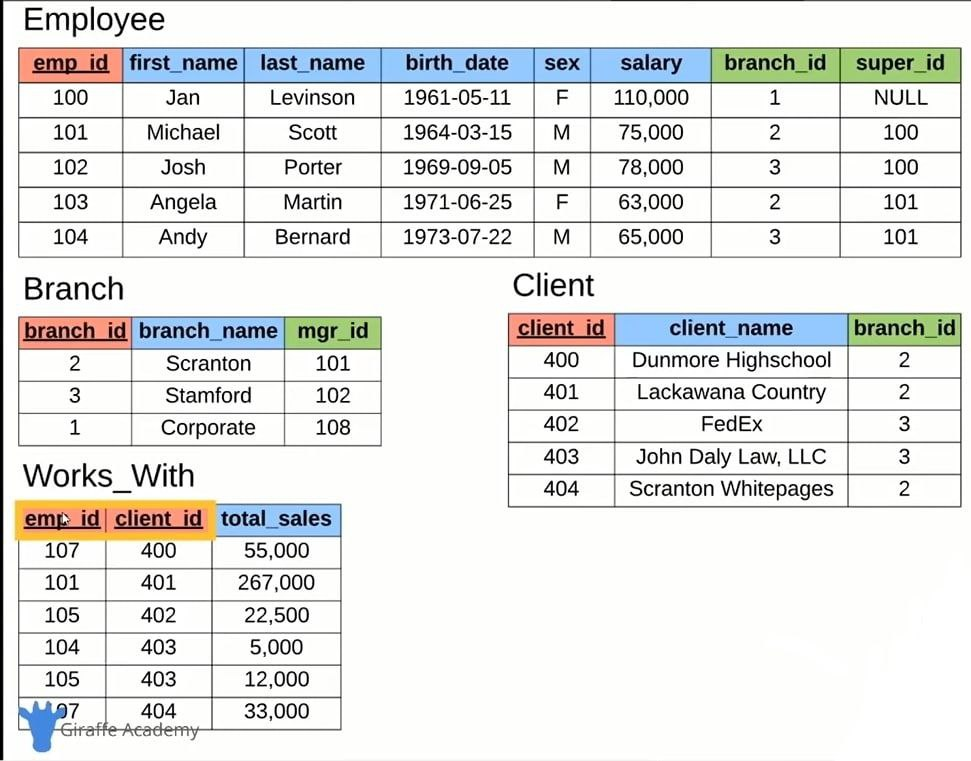
Designing company schema -
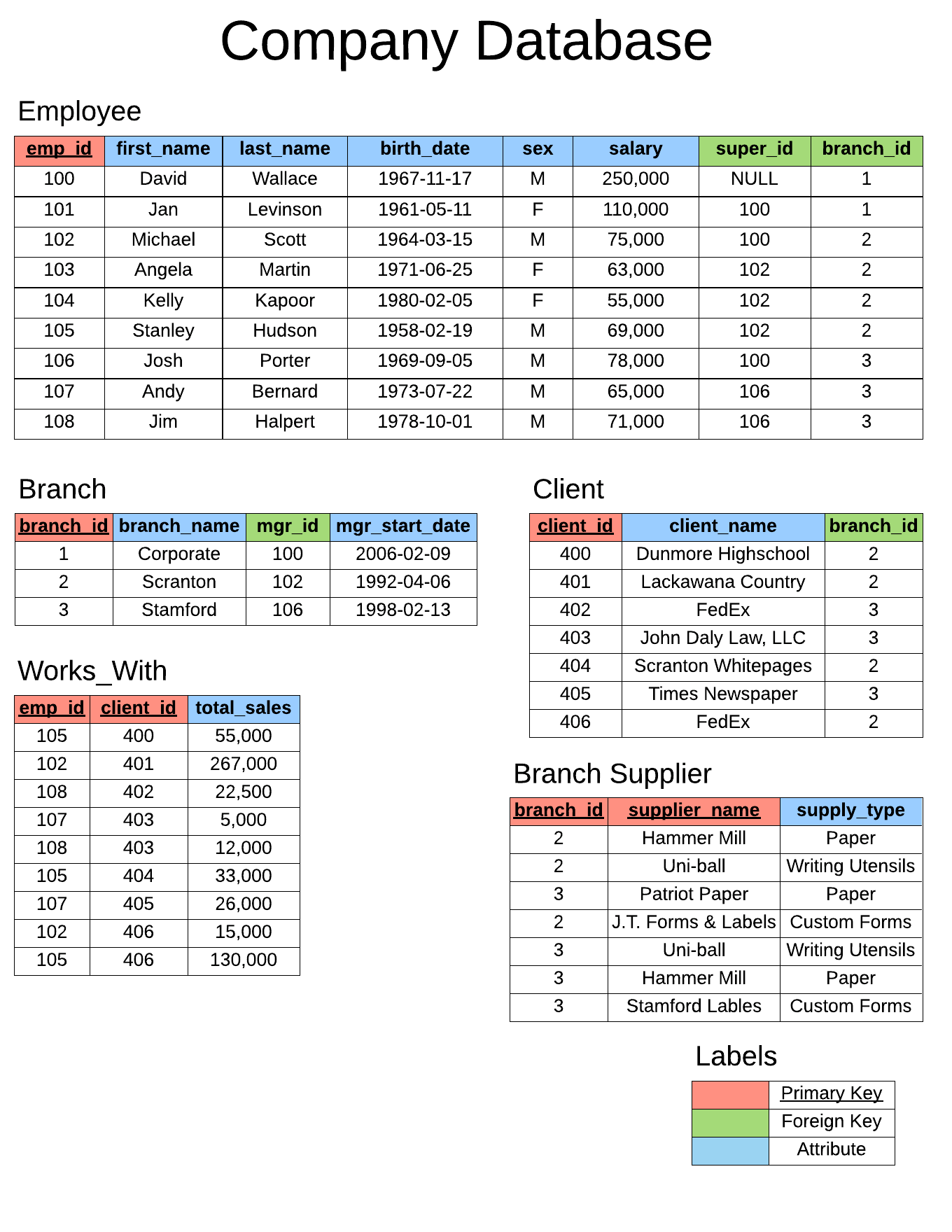
CREATE TABLE employee (
emp_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(40),
last_name VARCHAR(40),
birth_day DATE,
sex VARCHAR(1),
salary INT,
super_id INT,
branch_id INT
);
CREATE TABLE branch (
branch_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
branch_name VARCHAR(40),
mgr_id INT,
mgr_start_date DATE,
FOREIGN KEY(mgr_id) REFERENCES employee(emp_id) ON DELETE SET NULL
);
ALTER TABLE employee
ADD FOREIGN KEY(branch_id)
REFERENCES branch(branch_id)
ON DELETE SET NULL;
ALTER TABLE employee
ADD FOREIGN KEY(super_id)
REFERENCES employee(emp_id)
ON DELETE SET NULL;
SELECT * FROM employee;
CREATE TABLE client (
client_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
client_name VARCHAR(40),
branch_id INT,
FOREIGN KEY(branch_id) REFERENCES branch(branch_id) ON DELETE SET NULL
);
CREATE TABLE works_with (
emp_id INT,
client_id INT,
total_sales INT,
PRIMARY KEY(emp_id, client_id),
FOREIGN KEY(emp_id) REFERENCES employee(emp_id) ON DELETE CASCADE,
FOREIGN KEY(client_id) REFERENCES client(client_id) ON DELETE CASCADE
);
CREATE TABLE branch_supplier (
branch_id INT,
supplier_name VARCHAR(40),
supply_type VARCHAR(40),
PRIMARY KEY(branch_id, supplier_name),
FOREIGN KEY(branch_id) REFERENCES branch(branch_id) ON DELETE CASCADE
);
-- Corporate
INSERT INTO employee VALUES(100, 'David', 'Wallace', '1967-11-17', 'M', 250000, NULL, NULL);
INSERT INTO branch VALUES(1, 'Corporate', 100, '2006-02-09');
UPDATE employee
SET branch_id = 1
WHERE emp_id = 100;
INSERT INTO employee VALUES(101, 'Jan', 'Levinson', '1961-05-11', 'F', 110000, 100, 1);
-- Scranton
INSERT INTO employee VALUES(102, 'Michael', 'Scott', '1964-03-15', 'M', 75000, 100, NULL);
INSERT INTO branch VALUES(2, 'Scranton', 102, '1992-04-06');
UPDATE employee
SET branch_id = 2
WHERE emp_id = 102;
INSERT INTO employee VALUES(103, 'Angela', 'Martin', '1971-06-25', 'F', 63000, 102, 2);
INSERT INTO employee VALUES(104, 'Kelly', 'Kapoor', '1980-02-05', 'F', 55000, 102, 2);
INSERT INTO employee VALUES(105, 'Stanley', 'Hudson', '1958-02-19', 'M', 69000, 102, 2);
-- Stamford
INSERT INTO employee VALUES(106, 'Josh', 'Porter', '1969-09-05', 'M', 78000, 100, NULL);
INSERT INTO branch VALUES(3, 'Stamford', 106, '1998-02-13');
UPDATE employee
SET branch_id = 3
WHERE emp_id = 106;
INSERT INTO employee VALUES(107, 'Andy', 'Bernard', '1973-07-22', 'M', 65000, 106, 3);
INSERT INTO employee VALUES(108, 'Jim', 'Halpert', '1978-10-01', 'M', 71000, 106, 3);
INSERT INTO branch_supplier VALUES(2, 'Hammer Mill', 'Paper');
INSERT INTO branch_supplier VALUES(2, 'Uni-ball', 'Writing Utensils');
INSERT INTO branch_supplier VALUES(3, 'Patriot Paper', 'Paper');
INSERT INTO branch_supplier VALUES(2, 'J.T. Forms & Labels', 'Custom Forms');
INSERT INTO branch_supplier VALUES(3, 'Uni-ball', 'Writing Utensils');
INSERT INTO branch_supplier VALUES(3, 'Hammer Mill', 'Paper');
INSERT INTO branch_supplier VALUES(3, 'Stamford Lables', 'Custom Forms');
-- CLIENT
INSERT INTO client VALUES(400, 'Dunmore Highschool', 2);
INSERT INTO client VALUES(401, 'Lackawana Country', 2);
INSERT INTO client VALUES(402, 'FedEx', 3);
INSERT INTO client VALUES(403, 'John Daly Law, LLC', 3);
INSERT INTO client VALUES(404, 'Scranton Whitepages', 2);
INSERT INTO client VALUES(405, 'Times Newspaper', 3);
INSERT INTO client VALUES(406, 'FedEx', 2);
-- works_with
INSERT INTO works_with VALUES(105, 400, 55000);
INSERT INTO works_with VALUES(102, 401, 267000);
INSERT INTO works_with VALUES(108, 402, 22500);
INSERT INTO works_with VALUES(107, 403, 5000);
INSERT INTO works_with VALUES(108, 403, 12000);
INSERT INTO works_with VALUES(105, 404, 33000);
INSERT INTO works_with VALUES(107, 405, 26000);
INSERT INTO works_with VALUES(102, 406, 15000);
INSERT INTO works_with VALUES(105, 406, 130000);
- Some basic queries -
-- find all employees
SELECT * FROM employee;
-- find all clients
SELECT * FROM client;
-- find all employees salary sorted
SELECT *
FROM employee
ORDER BY salary DESC;
-- find all employees order by sex then name
SELECT *
FROM employee
ORDER BY sex, first_name, last_name;
-- find the first 5 employees in table
SELECT *
FROM employee
LIMIT 5;
-- find the first and last name of all employees
SELECT first_name, last_name
FROM employee;
-- find the forename and surname of all employees
SELECT first_name AS forename, last_name as surname
FROM employee;
-- find out all the different gender
SELECT DISTINCT sex
FROM employee;
SQL Functions -
-- find the number of employees
SELECT COUNT(emp_id)
FROM employee;
-- find the number of female employees born after 1970
SELECT COUNT(emp_id)
FROM employee
WHERE sex = 'F' AND birth_day >= '1971-01-01';
-- find the average of all employee salary
SELECT AVG(salary)
FROM employee;
-- find the sum of all employee salary
SELECT SUM(salary)
FROM employee;
-- find how many males and females are there
SELECT COUNT(sex), sex
FROM employee
GROUP BY sex;
-- find the total sales of each salesman
SELECT SUM(total_sales), emp_id
FROM works_with
GROUP BY emp_id;
Wildcard -
-- % = any # characters, _ = one character
-- find any client's who are an LLC
SELECT *
FROM client
WHERE client_name LIKE '%LLC'; -- if client_name looks like this,
-- % here indicates that any character can come before that but it ends with LLC.
-- find any branch suppliers who are in label business
SELECT *
FROM branch_supplier
WHERE supplier_name LIKE '%Label%';
-- find any employee born in october
SELECT *
FROM employee
WHERE birth_day Like '____-10%';
-- find any clients who are schools
SELECT *
FROM client
WHERE client_name LIKE '%school%';
Unions -
Union is a basic SQL operator used to combine the results of multiple SELECT statements into one.
Rules of using UNION -
- Should have same number of columns in each queries.
- Should also have similar data types.
-- find a list of employee and branch names
SELECT first_name
FROM employee
UNION
SELECT branch_name
FROM branch
UNION
SELECT client_name
FROM client;
-- find a list of all clients & branch suppliers' names
SELECT client_name, branch_id
FROM client
UNION
SELECT supplier_name, branch_id
FROM branch_supplier;
-- find the list of all the money spent or earned by the company
SELECT salary
FROM employee
UNION
SELECT total_sale
FROM works_with;
JOIN -
JOIN are used to combine rows of two or more tables based on a related column between them -
-- find all branches and name of their managers
SELECT employee.emp_id, employee.first_name, branch.branch_name
FROM employee
JOIN branch
ON employee.emp_id = branch.mgr_id;
Types of joins -
- Inner JOIN - Inner JOIN(simply JOIN) combines the rows from two table whenever they have shared column in common.
- LEFT JOIN - Includes all the rows from the left table (FROM statement one).
- RIGHT JOIN - Includes all the rows from the right table
- Full OUTER JOIN - Combination of LEFT JOIN and RIGHT JOIN.
Nested Queries -
-- find name of all employees who have
-- sold over 30,000 to a single client
SELECT employees.first_name, employees.last_name
FROM employee
WHERE employee.emp_id IN(
SELECT works_with.emp_id
FROM works_with
WHERE works_with.total_sales > 30000;
)
-- find all clients who are handled by the branch
-- that Micheal Scott manages
-- assume that you know Micheal's ID
SELECT client_name
FROM client
WHERE branch_id IN(
SELECT branch_id
FROM branch
WHERE mgr_id = 102
);
ON DELETE -
- ON DELETE SET NULL -
CREATE TABLE branch (
branch_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
branch_name VARCHAR(40),
mgr_id INT,
mgr_start_date DATE,
FOREIGN KEY(mgr_id) REFERENCES employee(emp_id) ON DELETE SET NULL
);
-- here mgr_id will becomes NULL when emp_id is deleted
CREATE TABLE branch (
branch_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
branch_name VARCHAR(40),
mgr_id INT,
mgr_start_date DATE,
FOREIGN KEY(mgr_id) REFERENCES employee(emp_id) ON DELETE CASCADE
);
-- here mgr_id wil get deleted when emp_id is deleted
Triggers -
Trigger is a block of SQL code which will define a certain action when a certain operation gets performed on the database.
DELIMETER $$
CREATE
TRIGGER my_trigger BEFORE INSERT
ON employee
FOR EACH ROW BEGIN
INSERT INTO trigger_test VALUES('added new employee');
END$$
DELIMETER ;
-- here we are changing delimeter to $$ sign then back to ;
-- Whenever a new value is inserted into employee table
-- 'added new employee' is added into trigger_test table
DELIMETER $$
CREATE
TRIGGER my_trigger BEFORE INSERT
ON employee
FOR EACH ROW BEGIN
INSERT INTO trigger_test VALUES(NEW.first_name);
END$$
DELIMETER ;
-- this one will add first_name value of new entry in trigger_test
-- Complex trigger
DELIMETER $$
CREATE
TRIGGER my_trigger BEFORE INSERT
ON employee
FOR EACH ROW BEGIN
IF NEW.sex = 'M' THEN
INSERT INTO trigger_test VALUES('added male employee')
ELSEIF NEW.sex = 'F' THEN
INSERT INTO trigger_test VALUES('added female employee')
ELSE
INSERT INTO trigger_test VALUES('added other employee')
END IF;
END$$
DELIMITER ;
-- functioning obvious
-- Delete a trigger
DROP TRIGGER my_trigger;