Disjoint Set Union (DSU)
- Only for undirected graphs.
Also called a union–find data structure or merge–find set, is a data structure that stores a collection of disjoint (non-overlapping) sets. Equivalently, it stores a partition of a set into disjoint subsets. It provides operations for adding new sets, merging sets (replacing them by their union), and it will be able to tell in which set a specific element is and finding a representative member of a set. The last operation allows to find out efficiently if any two elements are in the same or different sets.
The data structure allows you to do each of these operations in almost O(1) time on average.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Graph {
int V;
list<pair<int, int>> l;
public:
Graph(int V) { this->V = V; }
void addEdge(int u, int v) { l.push_back(make_pair(u, v)); }
// Find
int findSet(int i, int parent[]) {
// base case
if (parent[i] == -1) return i;
return findSet(parent[i], parent);
}
// Union
void unionSet(int x, int y, int parent[]) {
int s1 = findSet(x, parent);
int s2 = findSet(y, parent);
if (s1 != s2) parent[s1] = s2;
}
bool containsCycle() {
// DSU logic to check if graph contains cycle or not
int *parent = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
parent[i] = -1;
}
// interate over the edge list
for (auto edge : l) {
int i = edge.first;
int j = edge.second;
int s1 = findSet(i, parent);
int s2 = findSet(j, parent);
if (s1 != s2)
unionSet(s1, s2, parent);
else {
cout << "Same parents " << s1 << " and " << s2 << "\n";
return true;
}
}
delete[] parent;
return false;
}
};
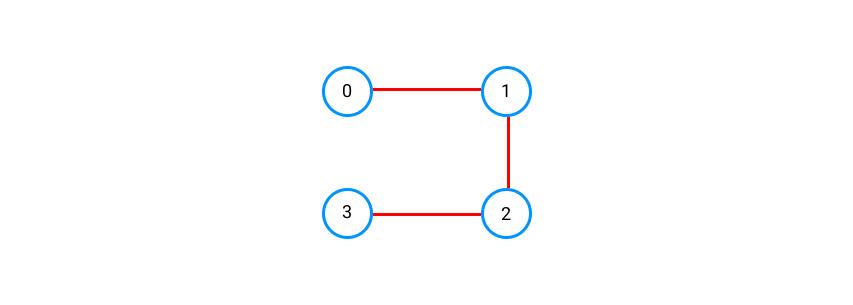
int main() {
Graph g(4);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 0);
cout << g.containsCycle();
return 0;
}
//Output
//Same parents 3 and 3
//1
Optimization :
- Path Compression Optimization in DSU (Find Fn).
- Union by Rank (Union Fn).
Path Compression Optimization :
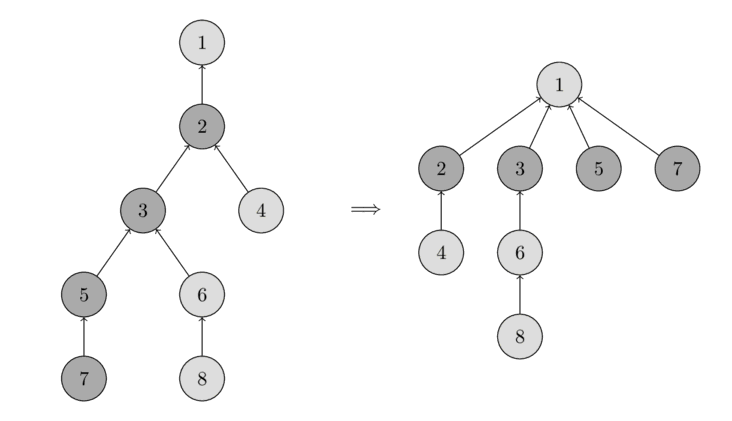
This optimization is designed for speeding up findSet.
int findSet(int i, int parent[]) { // Time = O(n)
// base case
if (parent[i] == -1) return i;
// path compression optimisation
return parent[i] = findSet(parent[i], parent);
}
Union By Rank (Balance optimization):
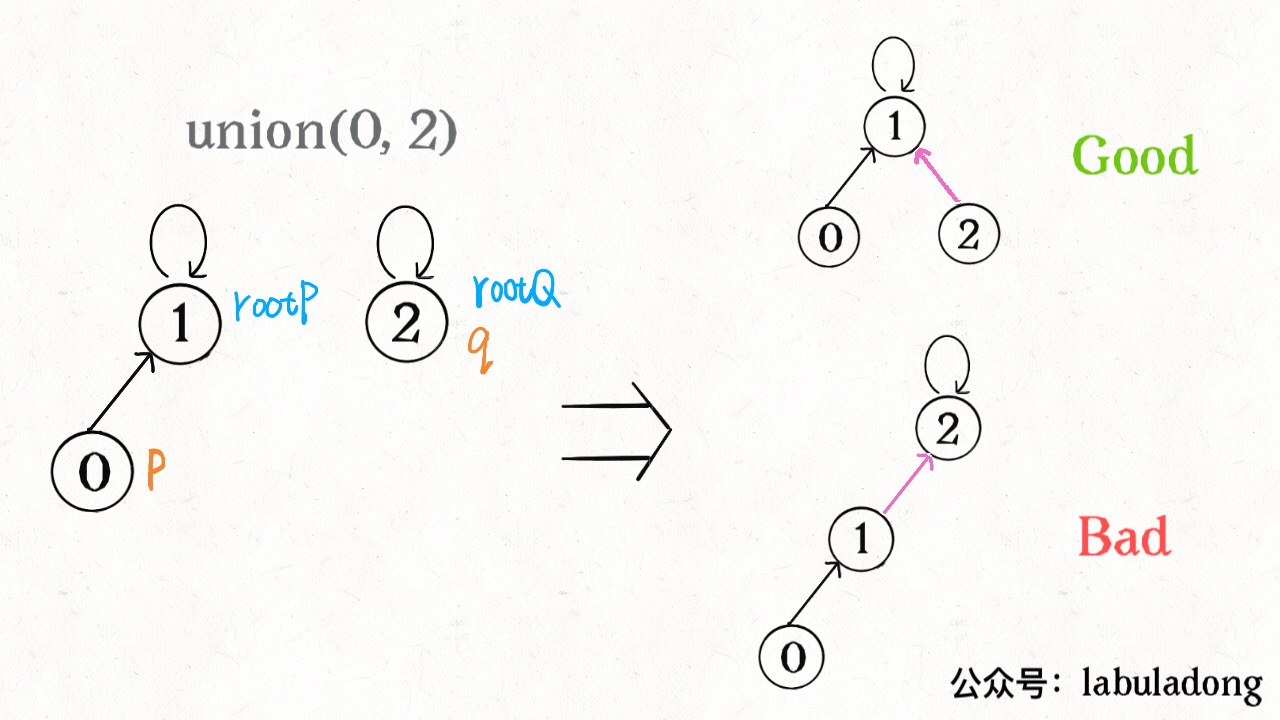
// dsu finding a cycle
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Graph {
int V;
vector<pair<int, int>> l;
public:
Graph (int n) {
V = n;
}
void addEdge(int x, int y) {
l.push_back({x, y});
}
//Find Function (optimized)
int find (int i, vector<int> &parent) {
if (parent[i] == -1) return i;
else return parent[i] = find (parent[i], parent);
}
//Union Function (optimized)
void unite (int s1, int s2, vector<int> &parent, vector<int> &rank) {
if (rank[s1] > rank[s2]) {
parent[s2] = s1;
rank[s1] += rank[s2];
} else {
parent[s1] = s2;
rank[s2] += rank[s1];
}
}
//contain cycle
bool containCycle () {
vector<int> parent(V, -1);
vector<int> rank(V, 1);
for (auto edge : l) {
int s1 = find (edge.first, parent);
int s2 = find (edge.second, parent);
if (s1 == s2) return true;
else unite(s1, s2, parent, rank);
}
return false;
}
};
int main() {
Graph g(3);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
cout << g.containCycle(parent); // 0
return 0;
}